- Atrás
- Sistema Integrado de Matrícula y Control Académico (SIMCA)
- Biblioteca
- Sistema de Información Vicerrectoría de Investigaciones (SIVRI)
-
Sistemas de Pagos arrow_right - Sistema de Contratación
- Solicitud de Mantenimiento
- Catálogo de Biblioteca
- Sistema de Atención y Soporte (SaTis)
- Banco de Aspirantes
- Sistema de Control Interno
- Sistema de Empadronamiento
- Sistema de Votaciones en Línea (SiVot)
- Sistema de Adquisición de Bienes (SAB)
- Atrás
- Vicerrectoría Académica
- Facultad de Artes
- Facultad de Ciencias Agrarias
- Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud
- Facultad de Ciencias Contables, Económicas y Administrativas
- Facultad de Ciencias Humanas y Sociales
- Facultad de Ciencias Naturales, Exactas y de la Educación
- Facultad de Derecho, Ciencias Políticas y Sociales
- Facultad de Ingeniería Civil
- Facultad de Ingeniería Electrónica y Telecomunicaciones
- Atrás
- Cursos de Extensión
-
Aumentar letra
-
Reducir letra
-
Aumentar Espaciado
-
Disminuir Espaciado
-
Escala de Grises
-
Contraste
-
Fuente Dislexia
-
Agrandar Cursor
-
Resaltar Enlaces
-
Restablecer
-
Centro de relevo
Home La Universidad Rectoría Oficina de Control Disciplinario Interno Autoridades Disciplinarias
Oficina de Control Disciplinario Interno
Área de Instrucción
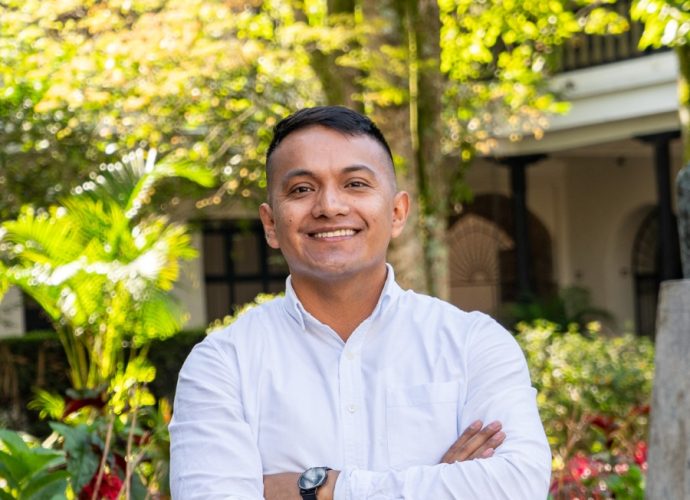
Profesión Especializado: Kevin Robinson Narváez Chilma
Correo electrónico: instrucciondisciplinaria@unicauca.edu.co
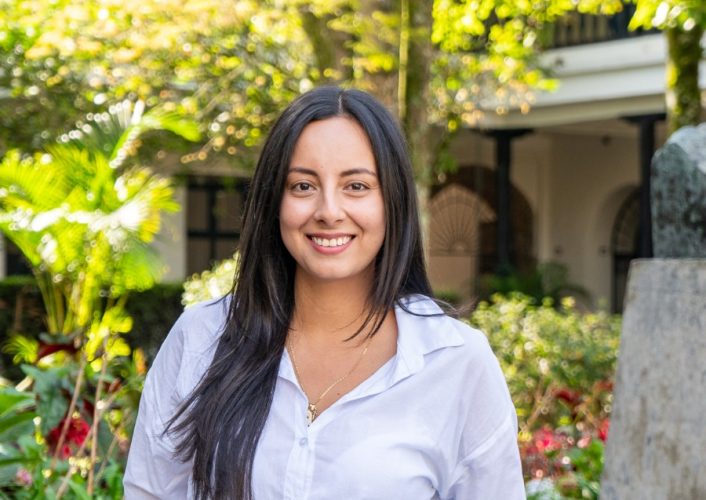


Área de Juzgamiento
Profesión Especializada: Tatiana Andrea Medina Muñoz
Correo electrónico: juzgamientodisciplinario@unicauca.edu.co
Otras Autoridades

Enlaces de interés
Contáctanos
Dirección: Calle 5 # 4 - 70 | Popayán, Colombia
Horario de atención:
Lunes a jueves de 8:00 a.m. a 5:00 p.m. - Viernes de 8:00 a.m. a 4:00 p.m.
Teléfono: +57 (602) 820 9900
Línea gratuita: 018000 949020
Notificaciones judiciales
Institución con Acreditación de Alta Calidad por 8 años, resolución MEN 6218 de 2019 - Vigilada MinEducación
-
Aumentar letra
-
Reducir letra
-
Aumentar Espaciado
-
Disminuir Espaciado
-
Escala de Grises
-
Contraste
-
Fuente Dislexia
-
Agrandar Cursor
-
Resaltar Enlaces
-
Restablecer
-
Centro de relevo
Universidad del Cauca
NIT. 891500319-2
Enlaces de interés
Contáctanos
Dirección: Calle 5 # 4 - 70 | Popayán, Colombia
Teléfono: +57 (602) 820 9900
Línea gratuita: 018000 949020
Peticiones, Quejas, Reclamos, Sugerencias y Felicitaciones
Correo: quejasreclamos@unicauca.edu.co
Notificaciones judiciales
Correo: procesos@unicauca.edu.co
Línea anticorrupción
Correo: anticorrupcion@unicauca.edu.co
Institución con Acreditación de Alta Calidad por 8 años, resolución MEN 6218 de 2019 - Vigilada MinEducación